- Liquidity
- A market is liquid when it has a high level of trading activity, allowing buying and selling with minimum price disturbance. Also a market characterized by the ability to buy and sell with relative ease. The New York Times Financial Glossary
* * *
1. ECONOMICS the amount of money in an economy at a particular time:• The central bank injected liquidity into the economy (= increased liquidity ) last month when it began repurchasing government bonds.
— see also money supply2. FINANCE when investments can easily be bought and sold on a particular financial market:• As investors learned in the last stock market crash, liquidity can disappear quickly when everyone tries to sell at once.
3. FINANCE ACCOUNTING the ability of a company to make payments to employees and suppliers, interest payments to banks etc:• Disappointing sales and resulting losses have caused liquidity problems.
4. BANKING the ability of a bank to pay back people and organizations that have put money in the bank and that want to take their money out:• Customers began withdrawing deposits, causing difficulties for the liquidity of the bank.
* * *
The ease with which financial instruments can be traded on a market and turned into cash. Markets or instruments are described as being liquid, and having depth or liquidity, if there are enough buyers and sellers to absorb sudden shifts in supply and demand without price distortions. The opposite of illiquid. The term can also be used loosely to describe cash flow in a business, so a company that has fallen into a liquidity trap may have growing orders and production but has run out of cash.► See also Illiquid.* * *
liquidity UK US /lɪˈkwɪdɪti/ noun [U]► ACCOUNTING, FINANCE the fact of being able to be changed into cash easily: »the liquidity of assets/investments
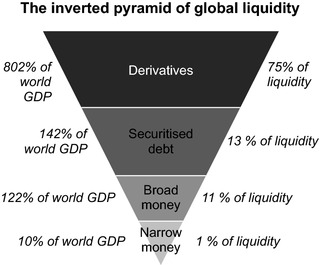 ► ACCOUNTING, FINANCE the state of having enough money or assets to pay any money that is owed: »
► ACCOUNTING, FINANCE the state of having enough money or assets to pay any money that is owed: »The business no longer has sufficient liquidity to meet its operational needs.
► (also market liquidity) FINANCE, STOCK MARKET the ability to buy or sell easily on a market, for example a market in shares or bonds: »They were forced to intervene, in order to maintain the liquidity of the market.
Financial and business terms. 2012.
